Estimated time: 4 minutes read
How to Guarantee Copyright in an NFT Contract?
In one of my previous articles, I described what royalties in an NFT Smart Contract are and the ways they can be established.
It is however necessary to address the main issue: how to guarantee that the beneficiary of the copyright will receive the stipulated amount after a commercial transaction.
The simplest scheme relies on the good practices of the marketplace where the transaction occurs. Cases like OpenSea and Rarible are among the platforms that reliably guarantee the strict fulfillment of the conditions set in the rights.
The following screenshot shows how royalties of a particular NFT collection are clearly displayed through the Rarible portal.
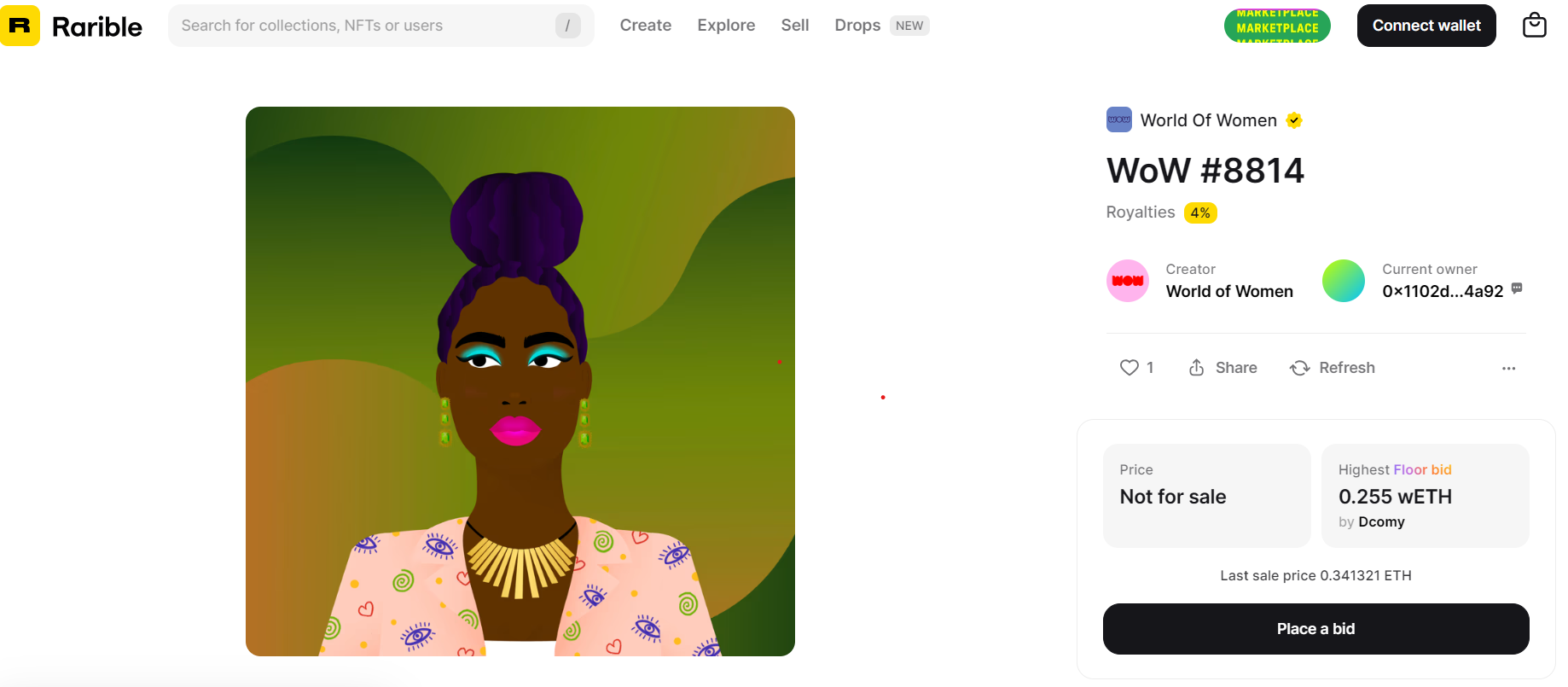
However, other marketplaces may consider copyright as something optional depending on the buyer’s preferences (for example, this is the case with Magic Eden) or even dispense entirely with copyright management.
To enforce copyright, LimitBreak introduced the Payment Processor protocol. This is a smart contract that manages on-chain the enforcement of royalties.
How does the Payment Processor work?
NFT collection creators can interact with an external registry (smart contract) validator to allow or block transfers of their NFTs based on the caller, the ‘from,’ and the ‘to’ of the transaction.
Version 5 of the Transfer Validator includes numerous improvements aimed at incorporating user feedback from earlier versions and leveraging the latest Ethereum updates brought by the Pectra upgrade.
This new version introduces the concept of list and security level.
The list defines which operators are authorized to perform token transfers on behalf of the user. The default list, list 0, is configured with those smart contracts that have proven their strict compliance with copyright. Among them, mainly OpenSea.
On the other hand, the security level is declared with a «rulesetId» to choose among several preconfigured options such as whitelist, blacklist, soulbound, or vanilla. The default list works with rulesetId=0 (whitelist type) configured with a series of additional options that define the basic behavior.
To ensure copyright compliance using the default configuration of the Payment Processor, it is only necessary to make sure that the «transferFrom» call of the NFT contract internally invokes the validateTransfer function of the TransferValidator.
/**
* @notice Apply the collection ruleset and options to a transfer operation of a creator token.
*
* @dev Modular rulesets with options determine the logic governing transfers.
*
* @dev Throws when the ruleset returns a non-zero error selector.
*
* @dev <h4>Postconditions:</h4>
* 1. Transfer is allowed or denied based on the ruleset.
*
* @param caller The address initiating the transfer.
* @param from The address of the token owner.
* @param to The address of the token receiver.
*/
function validateTransfer(address caller, address from, address to) external view;The TransferValidator smart contract is deployed at the same address across the most widely used blockchains.
How to add other trusted marketplaces?
We have seen that the default configuration allows transfers from OpenSea. However, there are other platforms equally respectful of copyright, such as Rarible.
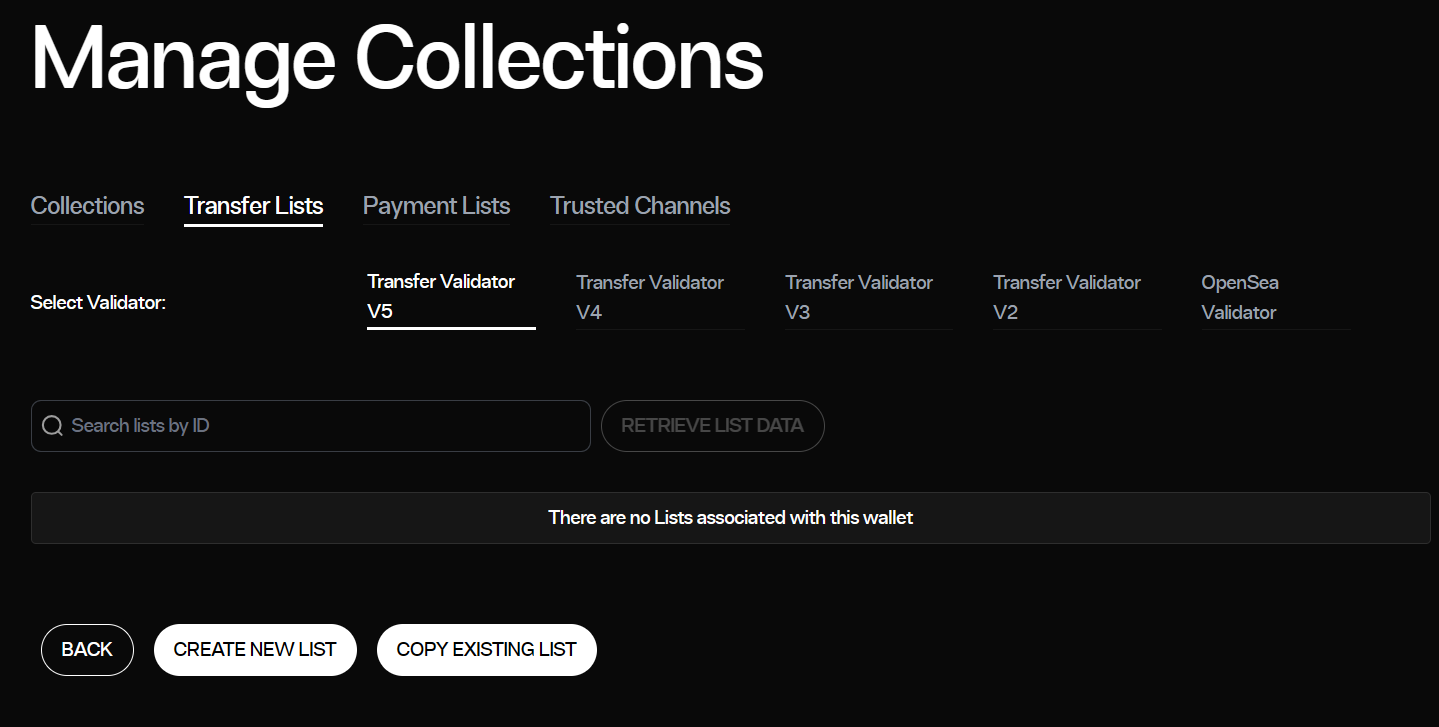
The Payment Processor protocol allows expanding the list of authorized smart contracts through several configurations. In our case, it is first necessary to create an ad-hoc list different from the default list (listId=0). The easiest way is to use the apptokens DApp. Connect the desired wallet on the target blockchain and go to «Manage my collections» to invoke the «createList» method of the TransferValidator and obtain the corresponding listId. The option is found under the «Transfer Lists» tab, with the «Create New List» button.
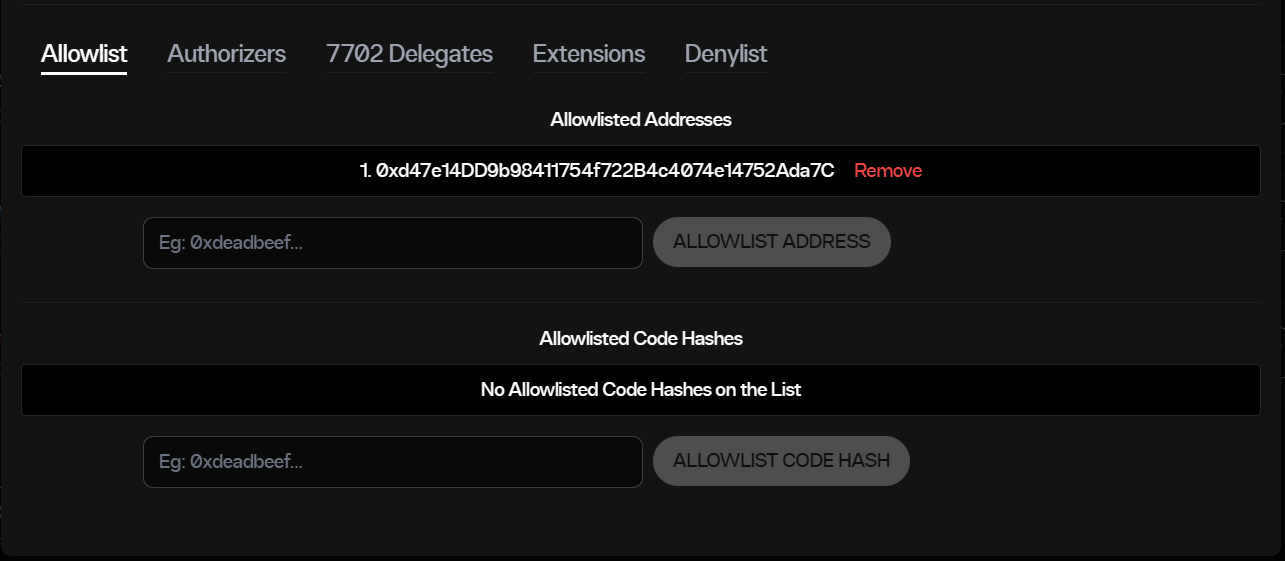
From there, it is necessary to configure the newly created list. This can be easily done from the same DApp. The option is to add to the «allowlist» the list of addresses of the smart contracts we want to authorize to carry out NFT transfers. In this example, it would be the address of the Rarible Transfer Proxy at 0xd47e14DD9b98411754f722B4c4074e14752Ada7C.
To enable the new list of authorized smart contracts in a token transfer for a particular NFT collection, the following methods of the TransferValidator must be invoked:
/**
* @notice Set the token type setting of a collection.
*
* @dev Throws when the caller is neither collection contract, nor the owner or admin
* of the specified collection.
*
* @dev <h4>Postconditions:</h4>
* 1. The token type of the specified collection is set to the new value.
* 2. A `SetTokenType` event is emitted.
*
* @param collection The address of the collection.
* @param tokenType The token type, ie: 721.
*/
function setTokenTypeOfCollection(
address collection,
uint16 tokenType
) external;
/**
* @notice Applies the specified list to a collection.
*
* @dev Throws when the caller is neither collection contract, nor the owner or admin
* of the specified collection.
* @dev Throws when the specified list id does not exist.
*
* @dev <h4>Postconditions:</h4>
* 1. The list of the specified collection is set to the new value.
* 2. An `AppliedListToCollection` event is emitted.
*
* @param collection The address of the collection.
* @param id The id of the newly created list
*/
function applyListToCollection(address collection, uint48 id) external;
/**
* @notice Set the ruleset id, global / ruleset options, fixed / custom ruleset for a collection.
*
* @dev Throws when the caller is neither collection contract, nor the owner or admin
* of the specified collection.
* @dev Throws when setting a custom ruleset to an unregistered ruleset address.
* @dev Throws when setting a ruleset id that is not bound to a ruleset address.
* @dev Throws when setting a custom ruleset with a managed ruleset id.
*
* @dev <h4>Postconditions:</h4>
* 1. The ruleset of the specified collection is set
* to the new value.
* 2. Global options and ruleset-specific options of the specified collection
are set to the new value.
* 3. A `SetCollectionRuleset` event is emitted.
* 4. A `SetCollectionSecurityPolicyOptions` event is emitted.
*
* @param collection The address of the collection.
* @param rulesetId The new ruleset id to apply. For whitelist type, set rulesetId=0
* @param customRuleset The address of the custom ruleset to apply. Must be address(0) unless
rulesetId is RULESET_ID_FIXED_OR_CUSTOM (255).
* @param globalOptions The global options to apply. Set a value of 8 so that default list extension
mode is enabled.
* @param rulesetOptions The ruleset-specific options to apply. Usually a 0 value.
*/
function setRulesetOfCollection(
address collection,
uint8 rulesetId,
address customRuleset,
uint8 globalOptions,
uint16 rulesetOptions
) external;
This page details the configuration options of a «Ruleset»
The most versatile and secure option is to call these methods of the TransferValidator directly after invoking the constructor of the NFT collection smart contract, from the same owner address. The most convenient approach is to define a Solidity interface with the method declarations and instantiate it at the known address of the TransferValidator smart contract.
Conclusion: enforcing copyright on-chain
In the latest articles, we have detailed the different ways royalties can be defined for token transfers in an NFT contract.
While it is always possible to delegate and trust the various actors involved in the token trade, such as a specific marketplace that allows off-chain rights management, given the decentralized nature of web3, it seems more appropriate to manage them without intermediaries directly on the blockchain (on-chain).
The initiative of LimitBreak aligns with this philosophy and allows content creators to safeguard their rights above the particular interests of exchanges and sales platforms, all in a decentralized way.
Have you ever had to ensure copyright enforcement in a smart contract? Did you choose on-chain protocols or rely on some trusted off-chain service?
If you are a creator and want to receive royalties without intermediaries, I can help you. Contact me and let’s talk about the available options. Thank you very much!




